The Copper-67 (Cu-67) Advantage
Cu-67 is a Versatile and Effective Therapeutic Radioisotope, Enabling an Ideal Theranostic Pair
-
Optimal Characteristics
Cu-67 has near-ideal characteristics as a therapeutic radioisotope (see table below)
-
Highly Effective and Versatile
Cu-67’s beta emission energy, half-life, imageable gamma energies, and centralized production make it highly effective and versatile
-
Ideal Theranostic Pair
Cu-67 labeled therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals may be paired with chemically identical Cu-64 or Cu-61 labeled imaging radiopharmaceuticals to produce a “perfect theranostic pair”
-
Versatile Chemistry
New chelator technologies provide chemical versatility, with the potential for Cu-67 to bind to a broad range of ligands
-
SPECT Imaging Capability
In addition to its therapeutic beta emissions, Cu-67 emits gamma radiation which can be imaged using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scanners, enabling assessment of cancer target binding, and informing decisions regarding subsequent patient treatment
How Do Cu-67 Radionuclide Features Benefit Patient Treatment?
93 keV & 185 keV gamma radiation energy
Cu-67 is imageable by Single Photon Computed Tomography (SPECT), and post-treatment SPECT images may predict therapeutic efficiency.
141 KeV mean beta radiation energy
0.6 mm beta particle emission range in tissue focuses energy primarily on cancer cells, minimizing “collateral damage” to non-target tissue.
61.8 hour half-life
Optimal treatment duration, with minimal hazards to patients, HCP’s and caregivers.
Centralized accelerator production - no reactors or generators needed
Scalable supply, low risk manufacturing process, direct shipping to sites in North America and Europe.
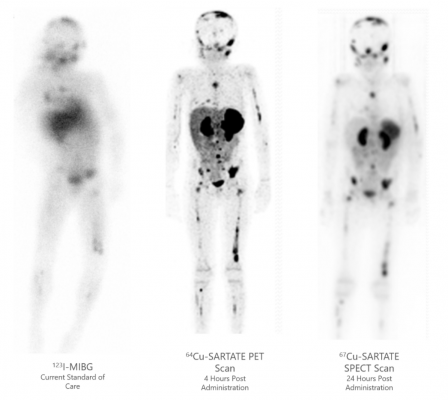
How do Cu-67 Characteristics Compare to Other Therapeutic Radioisotopes?
Cu-67 has ideal therapeutic radionuclide characteristics, particularly when paired with chemically identical Cu-64 or Cu-61 for diagnositc imaging.
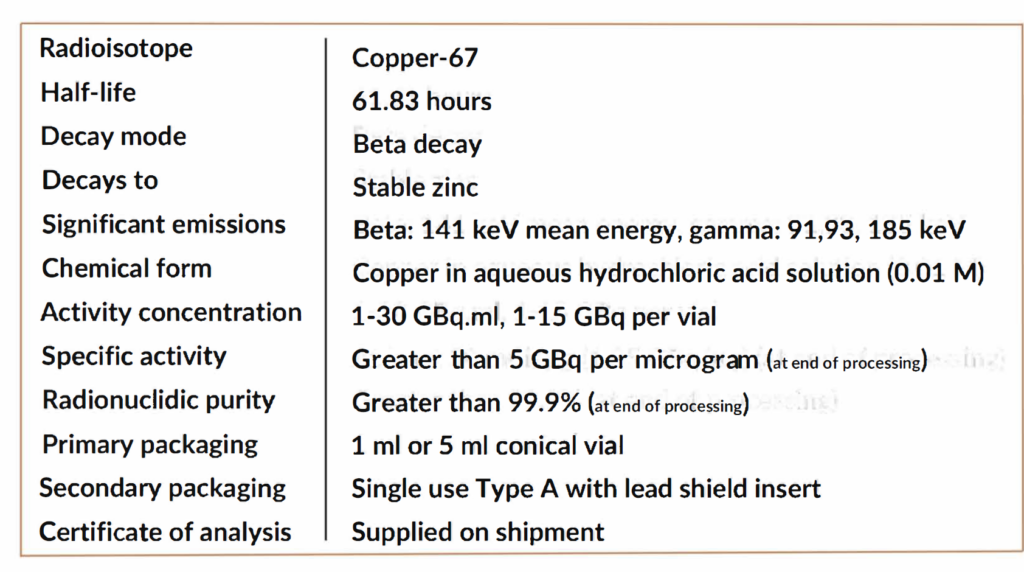
Batches of high-specific activity Cu-67 are now being made in North America with the following specifications:
- Cu-67 works as a therapeutic by emitting energized electrons (“beta radiation”) which collide with cancer cells, disrupting the cellular DNA and preventing those cells from replicating.
- Cu-67 is chemically bonded to a “ligand” molecule, which binds to cancer cells due to its affinity for specific receptors on the cancer cell surface.
- The ligand molecule bound to a therapeutic radioisotope (such as Cu-67) is known as a “therapeutic radiopharmaceutical”, and the treatment procedure is called “radioligand therapy”, or RLT.
- Cu-64 and Cu-61 work by emitting gamma radiation which can be detected by a PET scanner, which creates an image showing where the Cu-64/61 labelled molecule has targeted and accumulated.
- In addition to its therapeutic radiation, Cu-67 emits gamma radiation which can be imaged using widely available Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scanning. These SPECT images are not as clear or quantitative as the PET images using Cu-64/61, but they can be useful to confirm cancer cell uptake of the ligand, and to inform treatment decisions.
- Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals generate PET images which can identify cancer, locate tumors, assess the overall burden of disease (e.g.: gross tumor volume), provide information for treatment selection, assess therapeutic efficacy, and/or monitor disease status over time.
- Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals are sometimes used along with chemically similar or identical diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals, which differ primarily in the radioisotope used.
- The diagnostic radiopharmaceutical generates scans which may be used to select appropriate patients for treatment with the corresponding therapeutic radiopharmaceutical (radioligand therapy, or “RLT”).
- A diagnostic radiopharmaceutical used with a similar therapeutic radiopharmaceutical is known as a “theranostic pair”. When the pair are chemically identical, distribution in the patient’s body is expected to be identical. This optimizes the ability of the diagnostic radiopharmaceutical to predict the efficacy and specificity of the therapeutic radiopharmaceutical, and provides the most accurate images to assess treatment efficacy. When the diagnostic and therapeutic molecules are chemically identical, this is sometimes referred to as a “perfect theranostic pair”.
- Radiopharmaceuticals which incorporate Cu-64 or Cu-61 (diagnostic radioisotopes used with PET scanners) and Cu-67 (the chemically identical therapeutic radioisotope) are a “true theranostic pair”. A drug ligand with affinity for cancer cells may be labeled with Cu-64/61 to diagnose, locate and stage the disease, while the Cu-67 labeled ligand will seek out and treat the same cancer cells. The distribution of those 2 radiopharmaceuticals in the patient’s body will be identical.

